- WHY AVERTIUM?
-
-
Why Avertium?
Context over chaos. Disconnected technologies, siloed data, and reactive processes can only get you so far. Protecting businesses in today’s threat landscape demands more than a set of security tools – it requires context.
That's where Avertium comes in
-
Considering Microsoft?
Avertium Named Microsoft Security Solutions PartnerAvertium’s managed services for Microsoft Security Solutions is delivered through the company’s premium service: Fusion MXDR. Fusion MXDR includes 24x7 monitoring and management of Defender for Endpoint and Sentinel, threat intelligence, attack surface
monitoring, and vulnerability management for Microsoft Security customers. -
Latest Avertium News
How Gartner's 2024 Cybersecurity Trends Can Guide Your Cyber EffortsGartner has identified its six top cybersecurity trends for the year, and they’re ones that healthcare leaders should consider. Of the six trends, here are the ones that Avertium finds most instructive and beneficial.
-
-
- SOLUTIONS
-
-
Governance, Risk, + Compliance
GRC with context – not complexity. -
Attack Surface Management
No more blind spots, weak links, or fire drills. -
Threat Detection + Response
Detect, adapt, and attack with context. -
Microsoft Security Solutions
End-to-end support from strategy to daily operations to maximize your Microsoft Security.
-
-
- COMPANY
-
-
About Us
Security. It’s in our DNA. It’s elemental, foundational. Something that an always-on, everything’s-IoT-connected world depends on.
Helping mid-to-enterprise organizations protect assets and manage risk is our only business. Our mission is to make our customers’ world a safer place so that they may thrive in an always-on, connected world.
-
Latest Avertium News
How Gartner's 2024 Cybersecurity Trends Can Guide Your Cyber EffortsGartner has identified its six top cybersecurity trends for the year, and they’re ones that healthcare leaders should consider. Of the six trends, here are the ones that Avertium finds most instructive and beneficial.
-
-
- PARTNERS
-
-
Our Partners
Best-in-class technology from our partners... backed by service excellence from Avertium.
-
Partner Opportunity Registration
Interested in becoming a partner?
With Avertium's deal registration, partners can efficiently and confidently connect with Avertium on opportunities to protect your deals.
-
Latest Avertium Resource
Harnessing Copilot for Security: A Strategic Approach to Healthcare Cyber DefenseMicrosoft Copilot for Security analyzes and synthesizes high volumes of security data which can help healthcare cybersecurity teams do more with less.
-
-
- NEWS & RESOURCES
-
-
News & Resources
Dive into our resource hub and explore top
cybersecurity topics along with what we do
and what we can do for you. -
Latest Resource
Harnessing Copilot for Security: A Strategic Approach to Healthcare Cyber DefenseMicrosoft Copilot for Security analyzes and synthesizes high volumes of security data which can help healthcare cybersecurity teams do more with less.
-
-
- CONTACT
The Resurgence of Russian Threat Actor, NOBELIUM
Executive Summary
In 2020, SolarWinds was hit with a highly sophisticated supply-chain attack orchestrated by a nation-state threat actor. The Texas-based IT management and monitoring platform company was compromised when attackers slipped a malicious code into Orion (a software program that monitors various components within the company’s network) while it was being updated. The threat actors then used that update to deploy a massive cyberattack against the United States.
Today, we know the attackers as NOBELIUM, a Russian hacking group. Recently, NOBELIUM was seen making their rounds again, but this time their focus has shifted to software and cloud service resellers. Let’s take an in-depth look into NOBELIUM’s tactics and their most recent exploits.
nobelium and their tactics
When it comes to highly sophisticated malware attacks, NOBELIUM takes the lead. The SolarWinds breach was just the beginning of persistent malware attacks from the threat actor. In August 2021, NOBELLIUM was seen trying to exploit a cluster of Exchange vulnerabilities known as ProxyShell (CVE-2021-31207, CVE-2021-34523, CVE-2021-34473). The vulnerability allows threat actors to deploy web shells to unpatched Exchange servers for later access. Despite available security patches, organizations are still vulnerable due to not updating their servers.
In recent months, NOBELIUM has pivoted to attacking software and cloud service resellers. Their latest attacks include 3,000 individual accounts across more than 150 organizations. With those attacks, they used an established pattern of unique infrastructure and tools for each of their targets, enhancing their ability to go undetected for an extended period of time.
mAIN ATTACK METHODS FOR SOLARWINDS AND GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
Discovered by FireEye Inc., Nobelium used the SUNBURST backdoor, TEARDROP malware, and GoldMax malware to orchestrate their supply chain attack against SolarWinds. They also successfully breached nine United States government agencies (Department of Homeland Security, CISA, US Treasury, etc.) and 100 private companies using the same malware. After gaining access, NOBELIUM dug deeper into their victims’ networks by using a strategy that was simple, yet sophisticated. They used an initial attack that put them in the perfect position to compromise Microsoft 365 and Azure.
NOBELIUM studied Microsoft’s source code instructions for its Azure cloud programs related to identity and security, Intune management for mobile devices and applications, as well as it’s Exchange email programs. After some of the code was downloaded by SolarWinds’ customers, the threat actor had the freedom to hunt for security vulnerabilities, create copies with new flaws, and explore all the ways they could exploit customer installations. President and CEO of SolarWinds stated that there were an estimated 18,000 customers who downloaded the malicious code between March and June of 2020.
Additionally, NOBELIUM inserted software back doors for spying into network-management programs circulated by SolarWinds. The attackers also added new Azure identities, as well as greater rights to existing identities, and manipulated Microsoft programs to steal email. Two things needed to happen for the attack to work:
- People had to download the tainted update and deploy it.
- The compromised networks had to be connected to the Internet so attackers could communicate with their servers.
As a result of their success, NOBELIUM was able to infiltrate the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) – a government organization who is tasked with protecting federal computer networks from being attacked. This access gave NOBELIUM the ability to steal, alter, and destroy data. After being in the system, NOBELIUM removed all traces of their presence, making it difficult for investigators to prove who was behind the breach. Because NOBELIUM had the opportunity to roam the network undetected for nine months, it’s not clear whether they were simply reading emails or if they planted something destructive for use in the future.
NOBELIUM'S NEW BACKDOOR
After the SolarWind’s attack, chatter surrounding NOBELIUM died down. However, some researchers and analysts were continuing to keep a watchful eye on the threat actor despite their lack of activity - including Microsoft. In October 2021, Microsoft warned that NOBELIUM was once again attacking global IT supply-chains. This latest campaign was initially seen in May 2021 and there have already been 14 cases of compromise, with 140 companies being targeted.
While Microsoft estimated that the SolarWinds attack may have taken the efforts of up to 1,000 engineers, the latest attacks don’t appear to make use of specific vulnerabilities or security flaws. NOBELIUM appears to be relying on password spray, API abuse, phishing, and token theft to obtain credentials for accounts and privileged access to victims’ systems. Microsoft believes that NOBELIUM is using a piece of remote access malware called FoggyWeb with the objective of maintaining persistence on compromised Active Directory Federation Services servers (AD FS). This backdoor persistence was first observed in the wild in April 2021.
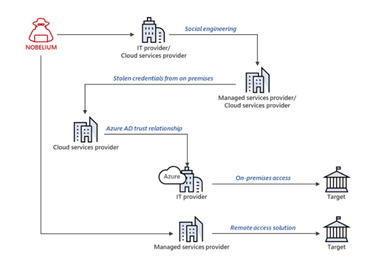
Image 1: New Access Across a Variety of Methods
Source: Microsoft.com
Although the success of NOBELIUM’s recent attacks is in the low single digits, Microsoft has warned 609 customers of 22,868 attack attempts between July 1 and October 19, 2021. Overall nation-state attack attempts totaled 20,500, including a NOBELIUM phishing campaign that impersonated USAID – an international development and humanitarian agency. Microsoft believes that NOBELIUM’s recent activity is Russia’s way of gaining long-term, systematic access to a variety of areas within the technology supply chain, so they can determine a process for attacking targets of interest for the Russian government.
FOGGYWEB
Since May 2021, NOBELIUM has targeted cloud service providers, managed service providers, and other IT services organizations within Europe and the United States. Microsoft reported that the group launched their recent campaign to exploit existing technical trust relationships between the provider organizations and the government, think tanks, and other companies they serve.
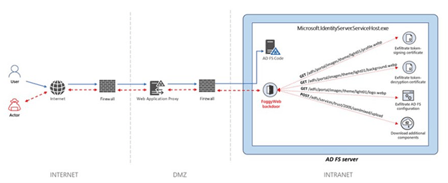
Image 2: FoggyWeb Backdoor
Source: Searchsecurity.techtarget.com
A passive and highly targeted backdoor, FoggyWeb is also capable of receiving malicious components from a command-and-control (C2) server and executes them on compromised servers. After compromising, Microsoft observed the threat actors dropping the following files:
- %WinDir%\ADFS\version.dll (backdoor)
- %WinDir%\SystemResources\Windows.Data.TimeZones\pris\Windows.Data.TimeZones.zh-PH.pri (loader)
Microsoft further observed NOBELIUM trying to exploit privileged accounts of service providers using FoggyWeb so they can move laterally in cloud environments and leverage trusted relationships, thus gaining access to downstream customers to further their attacks. After FoggyWeb is planted, NOBELIUM harvests credentials remotely and compromises the server. Once the server is compromised, the threat actor uses FoggyWeb to remotely exfiltrate the configuration database of the servers, decrypted token-signing certificate, and token-decryption certificate. NOBELIUM relies on this access to deepen infiltration with sophisticated malware tools. FoggyWeb ends up operating with administrator privileges.
nobelium's next victim
Until now, NOBELIUM has directed their attacks towards certain industries: technology, think tanks, telecommunications, military, and IT. The group has been operating for more than 10 years and they have a number of successful attacks under their belt, including the 2016 breach of the Democratic National Committee.
So, how can a threat actor who keeps changing their tactics be stopped? The answer to that question is a bit more complicated than following a list of “do’s and don’ts”. Kevin Mandia, the CEO of cyber security company, FireEye, stated that though we have only seen evidence of attacks on the previously mentioned industries, NOBELIUM has other targets that are less obvious like healthcare and utilities.
"I think utilities might be on that list. I think health care might be on that list. And you don't necessarily want to be on the list of fair game for the most capable offense to target you." Kevin Mandia – NPR.org
In order for organizations to prevent a cyberattack as sophisticated as NOBELIUM’s from disrupting their business operations, it’s important to stay three steps ahead. Fortunately, Microsoft was able to catch NOBELIUM’s recent campaign in its early stages and they were able to share information that could help cloud service resellers, technology providers, and customers. Time is everything when trying to prevent an attack and cyber security insurance will allow your organization to stay ahead.
avertium's recommendations
As a result of NOBELIUM’s new campaign, it’s important for organizations and administrators to have strict account security procedures and take further measures to keep environments safe. Avertium offers EDR and MDR services to help keep your organization safe.
- Our endpoint detection and response (EDR) is a platform of automated tools and capabilities that continuously monitor a system for suspicious activity within the security perimeter. These tools will recognize malicious activity from threat actors like NOBELIUM and will immediately alert the security team, which allows for rapid investigation and containment of attacks on endpoints.
- If you need a more advanced security solution, our managed detection and response (MDR) is the next step. MDR is an outsourced security control solution that includes the elements of EDR, enhanced with a range of fundamental security processes.
Avertium also recommends the following for NOBELIUM:
- Conduct regular inventories of all hardware in the environment.
- Conduct regular inventories of all software in the environment.
- Ensure multifactor authentication is in use.
- Ensure that user privileges, especially administrative user privileges are removed when not in use.
- Implement a Zero-Trust framework to neutralize any potential network intrusion.
- Implement and Enforce access control policies, particularly around sensitive information, and resources.
- Implement a vulnerability management program to increase awareness around existing vulnerabilities.
- Verify that all partner and 3rd-party contractors are following your security standards.
- Ensure System Logs are retained for as long as is possible to better enable Digital Forensics and Threat Hunting.
- Implement regular penetration testing to improve your security posture.
Microsoft Recommends the following for FoggyWeb Malware:
- Audit your on-premises and cloud infrastructure, including configuration, per-user, and per-app settings, forwarding rules, and other changes the actor might have made to maintain their access
- Remove user and app access, review configurations for each, and re-issue new, strong credentials following documented industry best practices.
- Use a hardware security module (HSM) as described in securing AD FS servers to prevent the exfiltration of secrets by FoggyWeb.
- Ensure only Active Directory Admins and AD FS Admins have admin rights to the AD FS system.
- Reduce local Administrators’ group membership on all AD FS servers.
- Require all cloud admins to use multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Ensure minimal administration capability via agents.
- Limit on-network access via host firewall.
- Ensure AD FS Admins use Admin Workstations to protect their credentials.
- Place AD FS server computer objects in a top-level OU that doesn’t also host other servers.
- Ensure that all GPOs that apply to AD FS servers apply only to them and not to any other servers. This limits potential privilege escalation through GPO modification.
- Ensure that the installed certificates are protected against theft. Don’t store these on a share on the network and set a calendar reminder to ensure they get renewed before expiring (expired certificate breaks federation auth). Additionally, we recommend protecting signing keys or certificates in a hardware security module (HSM) attached to AD FS.
- Set logging to the highest level and send the AD FS (and security) logs to a SIEM to correlate with AD authentication as well as Azure AD (or similar).
- Remove unnecessary protocols and Windows features.
- Use a long (>25 characters) and complex password for the AD FS service account. We recommend using a Group Managed Service Account (gMSA) as the service account, as it removes the need for managing the service account password over time by managing it automatically.
- Update to the latest AD FS version for security and logging improvements (as always, test first).
- When federated with Azure AD follow the best practices for securing and monitoring the AD FS trust with Azure AD.
Avertium Recommends the following for Sunburst:
- Sunburst is a SolarWinds digitally signed component of the Orion software framework that contains a backdoor that communicates via HTTP to third party servers. Avertium recommends the following:
- Monitor Services for unusual sign-ins, and/or changes to tokens and keys, especially inside O365 Logs.
- Reset/replace/re-issue all sensitive API key integrations, such as those leveraged by multi-factor, SAML integrations, website configuration files and others.
- Reset all credentials used by or stored in SolarWinds software.
- Treat all hosts monitored by the SolarWinds Orion monitoring software as compromised by threat actors and assume that further persistence mechanisms have been deployed.
- Rebuild hosts monitored by the SolarWinds Orion monitoring software using trusted sources.
Avertium Recommends the Following for ProxyShell:
- ProxyShell – install the latest Microsoft Exchange cumulative updates to patch.
MITRE TTPs:
Sunburst
- [T1218] Defense Evasion
- [T1047] Windows Management Instrumentation
- [T1546] Event Triggered Execution
- [T1562] Impair Defenses
- [T1560] Archive Collected Data
- [T1567] Exfiltration Over Web Service
FoggyWeb
- [T1598] Phishing for Information
- [T1071] Command and Control
- [T1001] Data Obfuscation
- [003] Protocol Impersonation
- [T1078] Valid Accounts
- [T113] External Remote Services
- [T1548] Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism
- [T1211] Exploitation for Defense Evasion
SIGMA Rules
- Suspicious Auditpol Usage
- AdFind Usage Detection
- UNC2452 Process Creation
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs):
FoggyWeb
- 5d5a1b4fafaf0451151d552d8eeb73ec
- 231b5517b583de102cde59630c3bf938155d17037162f663874e4662af2481b1
- 568392bd815de9b677788addfc4fa4b0a5847464b9208d2093a8623bbecd81e6
- da0be762bb785085d36aec80ef1697e25fb15414514768b3bcaf798dd9c9b169
- Trojan:Win32/FoggyWeb.A!dha (loader)
- Trojan:MSIL/FoggyWeb.A!dha (backdoor)
Sunburst
- com
- appsync-api.eu-west-1.avsvmcloud[.com]
- appsync-api.us-east-1.avsvmcloud[.com]
- 02af7cec58b9a5da1c542b5a32151ba1
- 08e35543d6110ed11fdf558bb093d401
- b91ce2fa41029f6955bff20079468448
- 019085a76ba7126fff22770d71bd901c325fc68ac55aa743327984e89f4b0134
- 292327e5c94afa352cc5a02ca273df543f2020d0e76368ff96c84f4e90778712
- databasegalore[.com]
- deftsecurity[.com[
- freescanonline[.com]
- highdatabase[.com]
- appsync-api.eu-west-1.avsvmcloud[.com]
- appsync-api.us-west-2.avsvmcloud[.com]
- a25cadd48d70f6ea0c4a241d99c5241269e6faccb4054e62d16784640f8e53bc
- 5e643654179e8b4cfe1d3c1906a90a4c8d611cea
- ebe711516d0f5cd8126f4d53e375c90b7b95e8f2
- digitalcollege[.org]
- globalnetworkissues[.com]
- virtualdataserver[.com]
ProxyShell
- C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\HWTJQDMFVMPOON.aspx
- C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\VJRFWFCHRULT.aspx
- C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\error.aspx
- D:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\FrontEnd\HttpProxy\owa\auth\HWTJQDMFVMPOON.aspx
- C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\nhmxea.aspx.aspx
- C:\inetpub\wwwroot\aspnet_client\supp0rt.aspx
- C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\FrontEnd\HttpProxy\owa\auth\d62ffcd688.aspx
- C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\FrontEnd\HttpProxy\owa\auth\Current\themes\resources\zaivc.aspx
Terms
Backdoor – A way to access a computer system or encrypted data that bypasses the systems customary security.
Command-and-Control (C2) – Systems used by attackers to communicate with compromised systems within a network.
Malware - A term used for viruses, worms, trojans, and other harmful computer programs. The programs are used by hackers to damage servers and networks for financial gain.
Password Spraying – A brute force attack where the attacker will brute force logins based on a list of usernames with default passwords on the application. Using one password against many different accounts.
Supporting Documentation
How Russia Used SolarWinds To Hack Microsoft, Intel, Pentagon, Other Networks : NPR
SolarWinds hackers, Nobelium, once again strike global IT supply chains, Microsoft warns | ZDNet
New sophisticated email-based attack from NOBELIUM - Microsoft Security Blog
The SolarWinds Hackers Used Tactics Other Groups Will Copy | WIRED
What is backdoor (computing)? - Definition from WhatIs.com (techtarget.com)
Password Spraying Attack | OWASP
eSentire | UPDATE: PoC Released, Active Exploitation of Exchange…
SolarWinds hackers studied Microsoft source code for authentication and email | Reuters
How Russia Used SolarWinds To Hack Microsoft, Intel, Pentagon, Other Networks : NPR
Microsoft warns of current Nobelium phishing campaign impersonating USAID | ZDNet
SolarWinds hackers Nobelium spotted using a new backdoor (techtarget.com)
SolarWinds Breach - SUNBURST Trojan - IOCs - AlienVault - Open Threat Exchange
FoggyWeb Backdoor - AlienVault - Open Threat Exchange
FoggyWeb: Targeted NOBELIUM malware leads to persistent backdoor - Microsoft Security Blog
New activity from Russian actor Nobelium - Microsoft On the Issues
Command-and-control servers: The puppet masters that govern malware (techtarget.com)
APPENDIX II: Disclaimer
This document and its contents do not constitute and are not a substitute for, legal advice. The outcome of a Security Risk Assessment should be utilized to ensure that diligent measures are taken to lower the risk of potential weaknesses be exploited to compromise data.
Although the Services and this report may provide data that Client can use in its compliance efforts, Client (not Avertium) is ultimately responsible for assessing and meeting Client's own compliance responsibilities. This report does not constitute a guarantee or assurance of the Client's compliance with any law, regulation, or standard.